The potential of evaporative cooling
When 1kg of moisture is delivered to the air by an adiabatic humidifier, 680W of evaporative cooling is achieved. As an adiabatic humidifier / cooler can provide up to 800kW of cooling for less than 1 kW of electricity, their potential for providing low cost cooling in air handling units is great.
There are three main strategies for in-duct evaporative cooling:
1kg of adiabatic humidification provides 680W of evaporative cooling
Direct evaporative cooling
Humidity is added to the incoming fresh air stream, reducing its temperature whilst increasing its humidity. This conditioned air is supplied directly to the room with a high percentage of the room air being exhausted, rather than re-circulated, to maintain a low humidity level in the room.
The amount of cooling that can be achieved depends upon the humidity level of the incoming air stream. Air with a lower humidity will absorb more moisture, resulting in a greater evaporative cooling effect.
Direct evaporative cooling in an air handling unit, raises the humidity and reduces the temperature
In-direct evaporative cooling
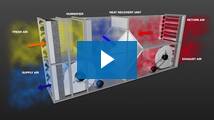
This strategy uses the outside air to cool an internal environment without any mixing of the internal and external air streams. Fresh outside air is run through the AHU's heat recovery (HR) unit and then exhausted, while the return air from the room is run through the HR unit before being re-introduced to the room. When the external air stream's temperature is cooler than the internal air stream, its cool thermal energy is transferred and cools the room.
By humidifying the external air stream prior to the HR unit, its temperature is reduced, enhancing the cooling capacity of the system. This allows an in-direct cooling strategy to be used even when the outside temperature is warmer than the desired supply condition to the room. A higher velocity on the external air stream than the internal further increases the cooling capacity of the system.
In-direct evaporative cooling reduces the temperature without internal and external air streams mixing or moisture being added to the internal air stream
Exhaust air evaporative cooling
The air extracted from the room is first cooled by the humidifier and then run through a HR unit before being vented outside. The cool thermal energy provided by the humidifier is transferred to the incoming air stream by the HR unit, cooling it by a few degrees and reducing the required load on DX air conditioning systems.
As there is no mixing of the humidified exhaust air and the incoming fresh air, there is no moisture added, so cooling occurs irrespective of the incoming air's humidity level.
Exhaust air cooling reduces the temperature of the incoming fresh air without adding moisture
Get free expert advice on AHU evaporative cooling.
Benefits of working with Condair on your evaporative cooling project:
- Comprehensive range of adiabatic humidifiers to suit any AHU strategy
- Ability to adapt a system for an AHU manufacturer's specific requirements
- Extensive experience in evaporative cooling projects around the world
- Comprehensive service of expert advice, system design, manufacture, supply, installation, commissioning, service and spares supply
- Low maintenance systems to minimise on-going service requirements
- World leading, innovative proven solutions
- Metronode Data Centres, Australia
- Truflow Spray Booths, Australia
- Drysys Spray Booths, Australia
- University of Sydney, Australia
- Sydney Opera House, Australia
- Microsoft, Ireland
- AirDesign (UK), UK
- Air Handling Systems Ltd, UK
- Barkell Air Handling Units, UK

Download brochure
You may also be interested in...

Evaporative humidifier provides cooling to packaged AHU

myCoolblue app

Condair ME evaporative humidifier & cooler